Is 40Hz Light and Sound Stimulation Therapy for Alzheimer's Disease Within Reach?
GemPages40Hz light and sound stimulation has emerged as a potential method to alleviate symptoms in Alzheimer's disease patients. Public opinion on this approach is divided: some believe it could be effective, others are skeptical and dismiss it as unfounded, while a third group remains open-minded, willing to try it since it seems harmless. Let's explore how this therapy has developed and examine whether it truly lives up to claims of effectively relieving Alzheimer's symptoms by delving into its history and the experimental evidence behind it.

Part 1: The Development of 40Hz Stimulation Therapy
2016: Researchers at MIT discovered that LED lights flickering at a 40Hz frequency could reduce beta-amyloid plaques in mouse brains. Using their specialized LED device, they were able to eliminate 40-50% of beta-amyloid protein in the mouse hippocampus within one hour, with longer treatment durations leading to greater clearance. [1]
2019: The same research team published another paper indicating that 40Hz sound stimulation could also clear beta-amyloid and improve cognition in Alzheimer's model mice. They found that after seven consecutive days of one-hour daily 40Hz sound exposure, the mice showed reduced beta-amyloid levels and a significant decrease in plaque count. [2]
2021: The team's data suggested that a regimen of one hour daily for six months could significantly slow disease progression in patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's. They reported an 84% slower decline in Activities of Daily Living (ADCS-ADL) scores, an 83% slower decline in Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores, and a 61% reduction in brain atrophy. In the same year, Cognito Therapeutics received a FDA device designation for this as a next-generation digital therapeutic for Alzheimer's disease.
Part 2: A Significant Setback for 40Hz Therapy
In 2023, a team from New York University published a paper in Nature Neuroscience expressing skepticism towards the 40Hz stimulation therapy, casting doubt on its efficacy.
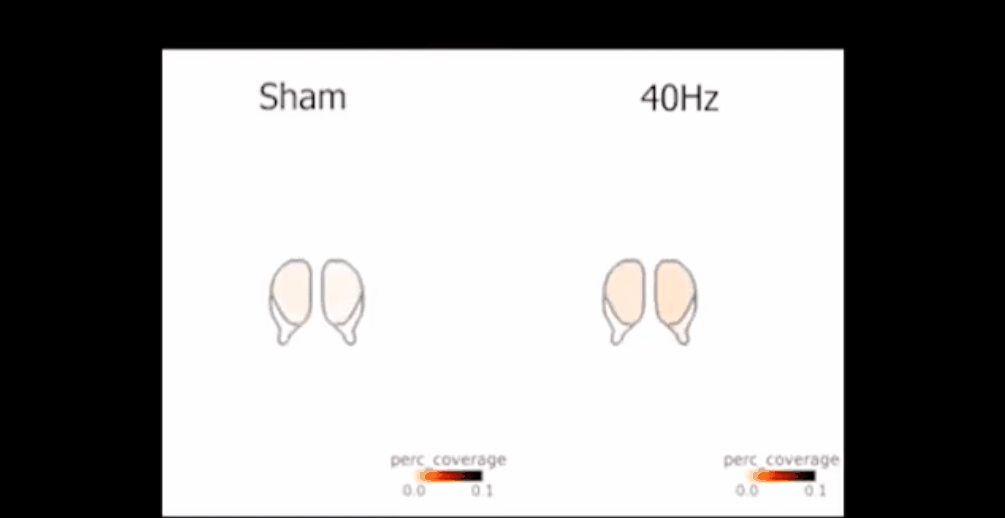
The researchers, through controlled experiments, found no significant changes in brain cells between test groups. Comparing various physiological parameters of brain cells before and after light stimulation revealed no measurable effects. Even after long-term testing in mice—one hour of daily exposure for seven consecutive days—no significant changes were observed.
The paper concluded that 40Hz light stimulation failed to induce brain waves in two different Alzheimer's mouse models and did not clear beta-amyloid (Aβ) protein from their brains.
The NYU researchers noted that 40Hz light stimulation might not be an effective mechanism for modulating activity in deeper brain structures, suggesting it may not be a universally applicable method for the diverse pathological presentations of Alzheimer's disease.
Part 3: The Latest Research Findings
A study published in Nature on February 28, 2024, proposed a new mechanism for 40Hz therapy. The research team found that 40Hz multisensory stimulation promotes the exchange between cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and interstitial fluid (ISF) in Alzheimer's model mice, accelerating the glymphatic clearance of amyloid proteins. [3]
Experiments in mice showed that after 40Hz multisensory stimulation, the influx of CSF and outflow of ISF increased significantly. This stimulation enhanced the glymphatic clearance of amyloid proteins. Within one hour of 40Hz stimulation, arterial pulsation in the mice increased markedly, with greater contraction amplitude and faster frequency. This accelerated arterial pulsation likely drives faster CSF flow in perivascular spaces.
Since 2016, research into 40Hz light and sound stimulation has yielded notable findings, showing some effectiveness in animal studies. The 2024 study, in particular, further supports the role of glymphatic transport in promoting beta-amyloid clearance.
Despite receiving FDA digital therapy designation, 40Hz stimulation therapy still faces significant challenges. These include the need for validation in larger animal studies, confirmation of its underlying mechanisms, extensive human clinical trials, and addressing broader questions about the causal role of beta-amyloid and tau proteins in Alzheimer's, as well as the involvement of research teams and commercial entities.
For Alzheimer's patients, as a non-invasive intervention, trying 40Hz stimulation under medical guidance and with safety assurances may be a reasonable consideration.
Conquering Alzheimer's disease remains a long and complex journey. For the general public, increasing awareness and adopting preventive measures like lifestyle adjustments and cognitive training are crucial. For those with mild cognitive impairment, early screening and non-pharmacological interventions, especially professional and systematic cognitive training, are vital to effectively slow disease progression.
[1] Hunter F. Iaccarino, Annabelle C. Singer, et al. Gamma frequency entrainment attenuates amyloid load and modifies microglia. Nature. 540, pages230–235 (2016).
https://www.nature.com/articles/nature20587
[2] Anthony J. Martorell, Abigail L. Paulson, et al. Multi-sensory Gamma Stimulation Ameliorates Alzheimer’s-Associated Pathology and Improves Cognition. Cell Press. Volume 177,lssue 2,P256-271.E22.
https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(19)30163-1
[3] Mitchell H. Murdock, Cheng-Yi Yang, et al. Multisensory gamma stimulation promotes glymphatic clearance of amyloid. Nature. 627, Pages149–156 (2024).
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07132-6




